The Best PHP Examples |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › download image hosting scripts paysite php scripts › The Best PHP Examples |
The Best PHP Examples
|
PHP is a server-side scripting language created in 1995 by Rasmus Lerdorf. PHP is a widely-used open source general-purpose scripting language that is especially suited for web development and can be embedded into HTML. What is PHP used for?As of October 2018, PHP is used on 80% of websites whose server-side language is known. It is typically used on websites to generate web page content dynamically. Use-cases include: Websites and web applications (server-side scripting)Command line scriptingDesktop (GUI) applicationsTypically, it is used in the first form to generate web page content dynamically. For example, if you have a blog website, you might write some PHP scripts to retrieve your blog posts from a database and display them. Other uses for PHP scripts include: Processing and saving user input from form dataSetting and working with website cookiesRestricting access to certain pages of your websiteThe largest Social Networking Platform, Facebook is written using PHP How does PHP work?All PHP code is executed on a web server only, not on your local computer. For example, if you complete a form on a website and submit it, or click a link to a web page written in PHP, no actual PHP code runs on your computer. Instead, the form data or request for the web page gets sent to a web server to be processed by the PHP scripts. The web server then sends the processed HTML back to you (which is where 'Hypertext Preprocessor' in the name comes from), and your web browser displays the results. For this reason, you cannot see the PHP code of a website, only the resulting HTML that the PHP scripts have produced. This is illustrated below:  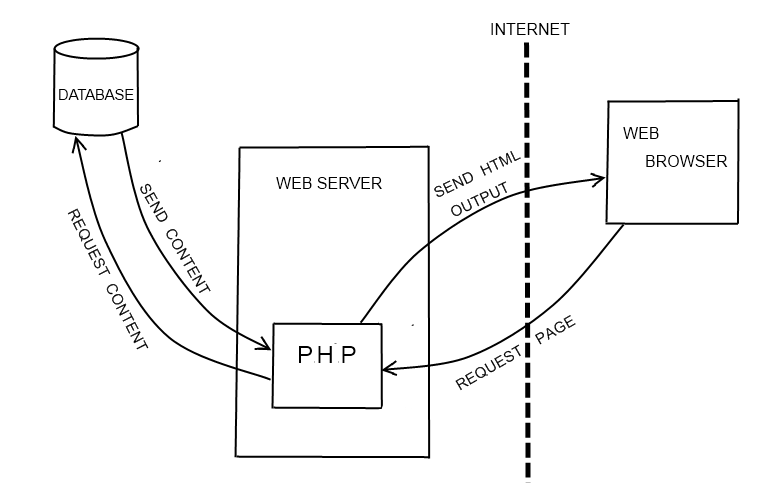 Source: https://github.com/xeroxism/ Source: https://github.com/xeroxism/PHP is an interpreted language. This means that when you make changes to your source code you can immediately test these changes, without first needing to compile your source code into binary form. Skipping the compilation step makes the development process much faster. PHP code is enclosed between the tags and can then be embedded into HTML. InstallationPHP can be installed with or without a web server. GNU/LinuxOn Debian based GNU/Linux distros, you can install by : sudo apt install phpOn Centos 6 or 7 you can install by : sudo yum install phpAfter installing you can run any PHP files by simply doing this in terminal : php file.phpYou can also install a localhost server to run PHP websites. For installing Apache Web Server : sudo apt install apache2 libapache2-mod-phpOr you can also install PHP, MySQL & Web-server all by installing XAMPP (free and open-source cross-platform web server solution stack package) or similar packages like WAMP PHP FrameworksSince writing the whole code for a website is not really practical/feasible for most projects, most developers tend to use frameworks for the web development. The advantage of using a framework is that You don't have to reinvent the wheel every time you create a project, a lot of the nuances are already taken care for youThey are usually well-structured so that it helps in the separation of concernsMost frameworks tend the follow the best practices of the languageA lot of them follow the MVC (Model-View-Controller) pattern so that it separates the presentation layer from logicPopular frameworksCodeIgniterLaravelSymfonyZendCakePHPFuelPHPSlimYii 2Basic SyntaxPHP scripts can be placed anywhere in a document, and always start with . Also, PHP statements end with a semicolon (;). Here's a simple script that uses the built-in echo function to output the text "The Best PHP Examples" to the page: Developer NewsThe output of that would be: Developer News The Best PHP ExamplesCommentsPHP supports several ways of commenting: Single-line comments:Multi-line comments:Case SensitivityAll keywords, classes, and functions are NOT case sensitive. In the example below, all three echo statements are valid: However, all variable names are case sensitive. In the example below, only the first statement is valid and will display the value of the $name variable. $NAME and $NaMe are both treated as different variables: VariablesVariables are the main way to store information in a PHP program. All variables in PHP start with a leading dollar sign like $variable_name. To assign a variable, use the = operator, with the name of the variable on the left and the expression to be evaluated on the right. Syntax: Rules for PHP variablesVariable declarations starts with $, followed by the name of the variableVariable names can only start with an upper or lowercase letter or an underscore (_)Variable names can only contain letters, numbers, or underscores (A-z, 0-9, and _). Other special characters like + - % ( ) . & are invalidVariable names are case sensitiveSome examples of allowed variable names: $my_variable$anotherVariable$the2ndVariablePredefined VariablesPHP has several special keywords that, while they are "valid" variable names, cannot be used for your variables. The reason for this is that the language itself has already defined those variables and they have are used for special purposes. Several examples are listed below, for a complete list see the PHP documentation site. $this$_GET$_POST$_SERVER$_FILESPHP Data TypesVariables can store data of different types such as: String ("Hello")Integer (5)Float (also called double) (1.0)Boolean ( 1 or 0 )Array ( array("I", "am", "an", "array") )ObjectNULLResourceStringsA string is a sequence of characters. It can be any text inside quotes (single or double): $x = "Hello!"; $y = 'Hello!';IntegersAn integer data type is a non-decimal number between -2,147,483,648 and 2,147,483,647. Rules for integers: Integers must have at least one digitIntegers must not have a decimal pointIntegers can be either positive or negative$x = 5; FloatsA float, or floating point number, is a number with a decimal point. $x = 5.01; BooleansA Boolean represents two possible states: TRUE or FALSE. Booleans are often used in conditional testing. $x = true; $y = false;ArraysAn array stores multiple values in one single variable. $colors = array("Magenta", "Yellow", "Cyan"); NULLNull is a special data type that can only have the value null. Variables can be declared with no value or emptied by setting the value to null. Also, if a variable is created without being assigned a value, it is automatically assigned null. Classes and ObjectsA class is a data structure useful for modeling things in the real world, and can contain properties and methods. Objects are instances a class, and are a convenient way to package values and functions specific to a class. PHP ResourceA resource is a special variable, holding a reference to an external resource. Resources are created and used by special functions. You can use getresourcetype() function to see resource type. Find the number of words in a stringThe strwordcount() function returns the number of words in a string: Reverse a StringThe strrev() function reverses a string: Search for text within a stringThe strpos() function searches for text in a string: Replace Text Within a StringThe str_replace() function replaces text in a string: ConstantsConstants are a type of variable in PHP. The define() function to set a constant takes three arguments - the key name, the key's value, and a Boolean (true or false) which determines whether the key's name is case-insensitive (false by default). A constant's value cannot be altered once it is set. It is used for values which rarely change (for example a database password OR API key). ScopeIt is important to know that unlike variables, constants ALWAYS have a global scope and can be accessed from any function in the script. $shopping_list[0] would return "eggs", $shopping_list[1] would return "milk", and $shopping_list[2] would return "cheese". Associative ArrayAn associative array is a list of values that are accessed via a key instead of index numbers. The key can be any value but it must be unique to the array. $student_scores['Joe'] would return 83, $student_scores['Frank'] would return 93, $student_scores['Benji'] would return 90. Multidimensional ArrayA multidimensional array is an array that contains other arrays. This lets you create complex data structures that can model a very complex group of data. Now you can get the first student's first_name with: $students[0]['first_name']Get The Length of an Array - The count() FunctionThe count() function is used to return the length (the number of elements) of an array: Sorting ArraysPHP offers several functions to sort arrays. This page describes the different functions and includes examples. sort()The sort() function sorts the values of an array in ascending alphabetical/numerical order (E.g. A, B, C, D, E... 1, 2, 3, 4, 5...) Output: Array ( [0] => camp [1] => code [2] => free )rsort()The rsort() functions sort the values of an array in descending alphabetical/numerical order (E.g. Z, Y, X, W, V... 5, 4, 3, 2, 1...) Output: Array ( [0] => free [1] => code [2] => camp )asort()The asort() function sorts an associative array, by its values, in ascending alphabetical/numerical order (E.g. A, B, C, D, E... 1, 2, 3, 4, 5...) Output: Array ( [two] => camp [one] => code [zero] => free )ksort()The ksort() function sorts an associative array, by its keys, in ascending alphabetical/numerical order (E.g. A, B, C, D, E... 1, 2, 3, 4, 5...) Output: Array ( [one] => code [two] => camp [zero] => free )arsort()The arsort() function sorts an associative array, by its values, in descending alphabetical/numerical order (E.g. Z, Y, X, W, V... 5, 4, 3, 2, 1...) Output: Array ( [zero] => free [one] => code [two] => camp )krsort()The krsort() function sorts an associative array, by its keys in descending alphabetical/numerical order (E.g. Z, Y, X, W, V... 5, 4, 3, 2, 1...) Output: Array ( [zero] => free [two] => camp [one] => code )FormsForms are a way for users to enter data or select data from the webpage. Forms can store data as well as allow the information to be retrieved for later use. To make a form to work in languages like PHP you need some basic attributes in html. In most cases PHP uses 'post' and 'get' super global variables to get the data from form. The 'method' attribute here tell the form the way to send the form data. Then the 'action' attribute tell where to send form data to process. Now the 'name' attribute is very important and it should be unique because in PHP the value of the name work as the identity of that input field. Checking Required InputsPHP has a few functions to check if the required inputs have been met. Those functions are isset, empty, and is_numeric. Checking form to make sure its setThe isset checks to see if the field has been set and isn't null. Example: $firstName = $_GET['firstName'] if(isset($firstName)){ echo "firstName field is set". ""; } else{ echo "The field is not set.".""; }Handling Form InputOne can get form inputs with global variables $POST and $GET. $_POST["firstname"] or $_GET['lastname'] |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |